Brainstorming Techniques for New Business Ideas: Embracing Design Thinking
- StartaSprout Team
- Mar 9, 2022
- 5 min read
Updated: Jan 4, 2024

Have you ever felt like you possessed all the qualities needed to become a successful entrepreneur, with the only missing piece being a brilliant business idea? That's where brainstorming enters the picture, precisely, an innovative method for generating new business ideas known as Design Thinking. As we navigate the dynamic entrepreneurial landscape, it's essential to explore creative techniques that can help us uncover groundbreaking solutions and stay ahead of the curve. So, buckle up, and let's delve into the exciting world of Design Thinking and its potential to revolutionize our ideation processes.
Understanding Design Thinking
At its core, Design Thinking is a human-centric problem-solving methodology that places users' needs, desires, and experiences at the forefront of innovation. It's a non-linear, iterative process that encourages us to challenge assumptions, embrace experimentation, and learn from failures. The beauty of Design Thinking lies in its adaptability to various industries and disciplines, making it an invaluable tool for generating transformative business ideas.

The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Design Thinking comprises five interconnected stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. While the process is not strictly linear, these stages provide a framework that can guide us through brainstorming and refining new business ideas.
Empathize
The first step in the Design Thinking process involves empathizing with your target users to gain a deep understanding of their needs, motivations, and pain points. This stage requires active listening, observation, and open-mindedness. By putting ourselves in the shoes of potential users, we can identify problems worth solving and lay the groundwork for innovative solutions.
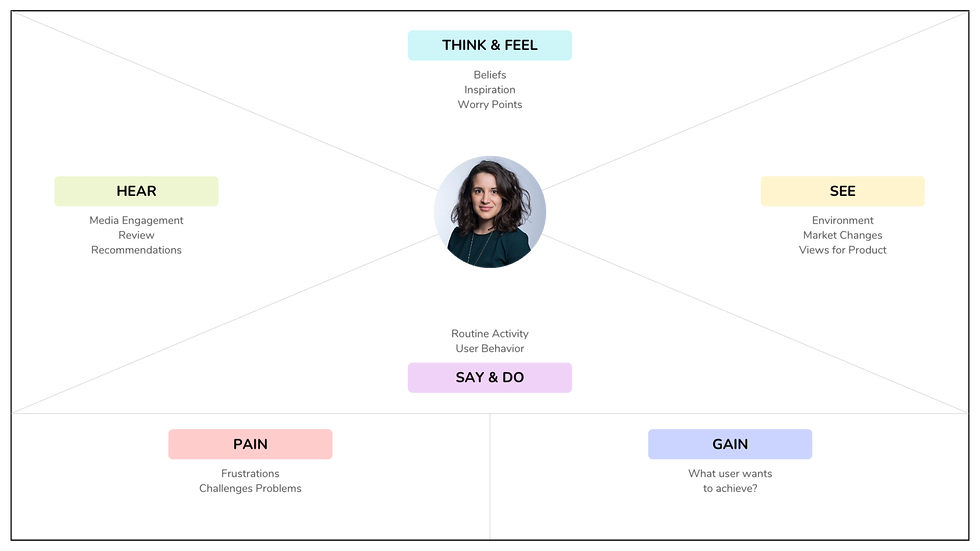
Tools
Interviews: Conduct one-on-one conversations with potential users or stakeholders to understand their needs and experiences.
Surveys: Create questionnaires to gather qualitative and quantitative data from a larger audience.
Observations: Watch users interact with existing products or services in their natural environment.
Tips
Develop open-ended questions to elicit honest and insightful responses.
Listen actively and avoid interrupting or leading the interviewee.
Document findings and look for patterns or commonalities among user experiences.
Define
After gathering valuable insights from the Empathize stage, we must synthesize the information to pinpoint specific user needs and challenges. In the Define stage, we craft clear problem statements that articulate users' requirements and guide our ideation process. This stage is crucial, as it ensures our business ideas remain grounded in real-world concerns and create tangible value for users.

Tools
Affinity Diagrams: Organize observations and insights into categories to reveal underlying patterns.
Empathy Maps: Visualize user needs, feelings, and thoughts to understand their perspectives better.
Problem Statements: Clearly articulate the problem you aim to solve by addressing the users' needs and insights.
Tips
Focus on the user's perspective, not your own assumptions.
Keep problem statements simple, concise, and human-centered.
Ensure the entire team understands and agrees on the problem definition.
Ideate
The Ideate stage is where the brainstorming magic happens. Here, we generate a plethora of potential solutions for the defined problem statements. Encourage wild, unconventional ideas and foster an environment where creativity can flourish. The more diverse the ideas, the better our chances of discovering truly groundbreaking business concepts. Remember to keep an open mind, suspend judgment, and embrace collaborative thinking.

Tools
Brainstorming Sessions: Encourage open and collaborative idea generation with your team.
Mind Maps: Visually organize ideas and explore their relationships.
SCAMPER Technique: Use prompts (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) to challenge existing ideas and generate new ones.
Tips
Create a safe and inclusive environment for idea sharing.
Encourage quantity over quality at this stage.
Defer judgment and evaluation until after the ideation phase.
Prototype
Once we have a range of promising ideas, it's time to bring them to life through prototyping. In this stage, we create tangible representations of our solutions, be it physical products, digital mockups, or service blueprints. Prototyping allows us to visualize and refine our ideas, making it easier to identify potential flaws, improvements, and opportunities for innovation.

Tools
Low-fidelity Prototypes: Create simple, physical, or digital representations of your ideas (e.g., sketches, wireframes, or cardboard models).
Storyboards: Visualize user interactions with your solution through a series of illustrations or images.
Role-Playing: Act out user scenarios to better understand their experience with your solution.
Tips
Embrace an iterative mindset and be prepared to refine your prototypes based on feedback.
Focus on testing specific aspects of your solution rather than creating a polished product.
Encourage collaboration and input from team members and users during prototyping.
Test
Finally, we arrive at the Test stage, where we evaluate the effectiveness of our prototypes by gathering user feedback. This stage involves iterative experimentation as we modify our solutions based on user insights and continually improve our business concepts. The Test stage is an ongoing process, encouraging us to stay responsive to user needs and maintain a growth mindset.

Tools
Usability Testing: Observe users as they interact with your prototype and gather feedback.
A/B Testing: Compare two or more prototypes to determine which performs better.
Feedback Sessions: Facilitate user and stakeholder discussions to gather insights and suggestions.
Tips
Develop clear criteria for evaluating your prototypes.
Be open to criticism and embrace the possibility of revisiting earlier stages.
Document findings, iterate on your solution, and continue testing until you reach a satisfactory result.
Harnessing Design Thinking for Business Ideation
By embracing Design Thinking, we can unlock a treasure trove of creative possibilities for new business ideas. This approach fosters empathy, innovation, and collaboration, empowering us to develop solutions that resonate with users and stand out in the competitive marketplace.
As we embark on our entrepreneurial journeys, it's vital to remember that Design Thinking is not a one-size-fits-all formula. Instead, it's a flexible, adaptable mindset that can help us navigate the complex process of business ideation. By adopting this human-centric approach, we can build a strong foundation for success and drive meaningful change in our industries.

Conclusion
As we strive to generate fresh business ideas in an increasingly competitive landscape, Design Thinking offers a valuable and proven framework for success. Focusing on empathy, experimentation, and iterative learning allows us to uncover new opportunities and create solutions that genuinely address our users' needs. Effective brainstorming hinges on our willingness to think outside the box, challenge assumptions, and embrace collaboration.
To foster an environment that nurtures open-mindedness, collaboration, and iterative learning, it's essential to embrace failure as an opportunity to grow, encourage risk-taking, and maintain flexibility in our approach. This mindset creates a breeding ground for exceptional business ideas that can disrupt industries and leave a lasting impact.
So, let's harness the power of Design Thinking, embrace the spirit of exploration, curiosity, and collaboration, and let these guiding principles lead us to discover groundbreaking business ideas that will reshape our industries and improve the lives of our users. Here's to the next wave of innovation and the entrepreneurs who bring it to life!
Happy brainstorming, and until next time, dear readers!

Comentarios